O.K. like I said in my previous post, B.A.T.M.A.N.
need an interface to run.so in this post we gone a cover that part.
First you need to check your current interface
by using this command,
iwconfig
If you see wlan0 there you are ready to go.
But if you doesn’t see make sure Wi-Fi is enabled. And identified your Wi-Fi
interface.
I made a small script that all the necessary
commands needed to active B.A.T.M.A.N.
You can put this script (it’s a sh file) in
/usr/local/sbin/ and execute it any ware you in.
By typing,
rockman.sh start
When you want to stop B.A.T.M.A.N. just type,
rockman.sh stop
And if you need help,
rockman.sh --help
You can download it from HERE or this is the
source code of my script,
#Copyright © RockMan#!/bin/bash#Your Wi-Fi interface name.IFACE=wlan0#Any essid name you want but need to be same for all B.A.T.M.A.N. nodes.ESSID=rockman2#I'm using channel 1.CHANNEL=1#This also must be same for all nodes.CELLID=02:12:34:56:78:9A#My ip address (must NOT be same for nodes, you know why).IPADD=10.0.1.15NETMASK=255.255.255.0#If you need help.if [ “$1” = “—help” ]; thenecho “[start](default) or [stop]”echo “your network devices:”lspci|grep -i netexitfiNETWORKMANAGER=”service network-manager”#Some distributions have like this.#NETWORKMANAGER=”/etc/init.d/network-manager”#Check whether you have root permissions or not.if [ “$(whoami &2>/dev/null)” != “root” ] && [ “$(id -un &2>/dev/null)” != “root” ] ; thenecho “Oops you must be root to run this script!”; exit 1fiif [ “$1” = “stop” ]; thenecho “Resuming normal networking...”echo “Restarting network-manager...”$NETWORKMANAGER restartecho “turning wlan iface off”batctl if del $IFACEsleep 10echo “OK”echo “It can take a few minutes until network-manager gets a new route”echoexitelif [ “$1” = “restart” ]; thenecho “Not implemented. Call this script first with stop and then with start”exitelse # “start”echo “Stopping network-manager…”$NETWORKMANAGER stopecho “plz wait…”sleep 10echo “Turning wlan iface off”ifconfig $IFACE downecho “Set maximal transfer unit from standard 1500 to 1528”ifconfig $IFACE mtu 1528echo “Turn wlan encryption off”iwconfig $IFACE enc offecho “Start ad-hoc mode”iwconfig $IFACE mode ad-hoc essid $ESSID ap $CELLID channel $CHANNELecho “Loading module into kernel”modprobe batman-advecho “Adding iface to batman”batctl if add $IFACEecho “Turning wlan iface on”ifconfig $IFACE upecho “Turning batman iface on”ifconfig bat0 $IPADD netmask $NETMASK upecho “ESSID $ESSID on $IFACE should be ready”echo “Now B.A.T.M.A.N. is up and running successfully !”echo "To resume normal networking call this script with option stop"echofi
Now it’s running. You can see batman is
flying over your head. Ha Ha Ha…
If you type “dmesg” you see some packets are
sending time to time. Or you can monitor those packets (DHCP REQUESTS) via
wireshark. Try that also.
And you can check current connected nodes
using this command,
batctl o
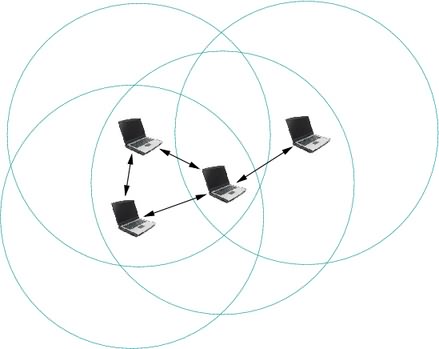
If you have connected to other nodes try to
ping to those nodes. If you do so your network is established.
Here is some additional but useful part by
using B.A.T.M.A.N. protocol.
If one node has internet connectivity you can
share it among others. Yes other nodes can access internet through that
internet node. By using this commands,
dhclient bat0
So if have any unexpected errors, please informed
me.\m/










No comments:
Post a Comment